Inflation may be of different forms, such as:
Demand Pull Inflation
• When in an economy aggregate demand exceeds aggregate supply.
• Aggregate demand may increase due to an increase in money supply, or money income or public expenditure.
• The idea of demand inflation is associated with full employment when supply cannot be altered.
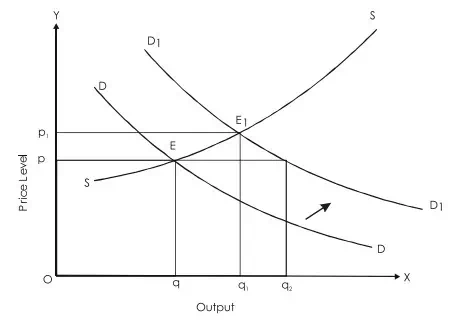
• In this graph SS and DD are aggregate supply and demand curves.
• Op and Oq are equilibrium price and equilibrium output.
• Due to exogenous causes demand curves shifts right-wards to D1 D1 .
• At the current price Op, demand increase by qq2 .
• But supply is Oq.
• Excess demand qq2 put pressure on price, which gradually rises from Op to Op1 .
• At this price a new equilibrium is achieved where Demand = Supply.
• The excess demand is eliminated by fall in demand and rise in supply arising out of rise in price.





