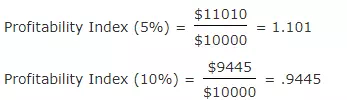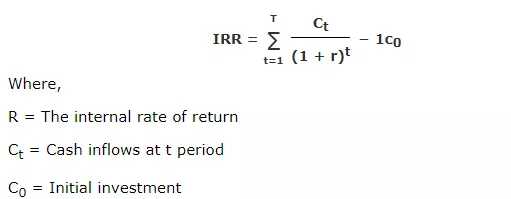Discounted cash flow techniques consider time value of money and are therefore also known as modern techniques.
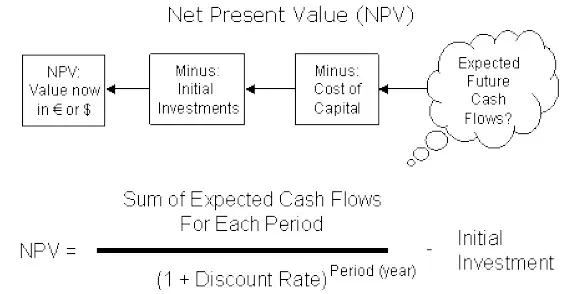
Net Present Value (NPV)
The net present value is one of the discounted cash flow techniques. It is the difference between the present value of future cash inflows and the present value of the initial outlay, discounted at the firm’s cost of capital. It recognizes the cash flow streams at different time intervals and can be computed only when they are expressed in terms of common denominator (present value). Present value is calculated by determining an appropriate discount rate. NPV is calculated with the help of equation.
NPV = Present value of cash inflows − Initial investment.
Advantages
NPV is considered as the most appropriate measure of profitability. It considers all the years of cash flow, and recognizes the time value for money. It is an absolute measure of profitability that means it gives output in terms of absolute amount. The NPVs of the projects can be added together which is not possible in other methods.
Profitability Index (PI)
Profitability index method is also known as benefit cost ratio as numerator measures benefits and denominator measures cost like the NPV approach. It is the ratio obtained by dividing the present value of future cash inflows by the present value of cash outlays. Mathematically it is defined as −
Advantages
In a capital rationing situation, PI is a better evaluation method as compared to NPV method. It considers the time value of money along cash flows generated by the project.
| Present Cash Value | |||
| Year | Cash Flows | @ 5% Discount | @ 10% Discount |
| 0 | $ -10,000.00 | $ -10,000.00 | $ -10,000.00 |
| 1 | $ 2,000.00 | $ 1,905.00 | $ 1,818.00 |
| 2 | $ 2,000.00 | $ 1,814.00 | $ 1,653.00 |
| 3 | $ 2,000.00 | $ 1,728.00 | $ 1,503.00 |
| 4 | $ 2,000.00 | $ 1,645.00 | $ 1,366.00 |
| 5 | $ 5,000.00 | $ 3,918.00 | $ 3,105.00 |
| Total | $ 1,010.00 | $ -555.00 |
Internal Rate of Return (IRR)
Internal rate of return is also known as yield on investment. IRR depends entirely on the initial outlay of the projects which are evaluated. It is the compound annual rate of return that the firm earns, if it invests in the project and receives the given cash inflows. Mathematically IRR is determined by the following equation −
Example −
| Internal Rate of Return | |
| Opening Balance | -100,000 |
| Year 1 Cash Flow | 110000 |
| Year 2 Cash Flow | 113000 |
| Year 3 Cash Flow | 117000 |
| Year 4 Cash Flow | 120000 |
| Year 5 Cash Flow | 122000 |
| Proceeds from Sale | 1100000 |
| IRR | 9.14% |
Advantages
IRR considers the total cash flows generated by a project over the life of the project. It measures profitability of the projects in percentage and can be easily compared with the opportunity cost of capital. It also considers the time value of money.