Definition
Supply of a commodity can be defined as the amount of goods that producers are willing to supply / sell at a given price.
Supply and Price
Price usually is a major determinant in the quantity supplied. In virtually all cases supply increases as price increases and vice versa.
This is because producers want to make profit.
– If the good is sold at a high price they want more quantities of it to be sold and they will make
more profit.
– and if it is sold at a lower price they will either make very less profit or a loss.
Supply Schedule

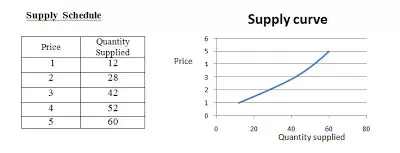
Supply curve shows the relationship between supply and price.
supply curve displays the quantity supplied on the x-axis as the independent variable and price on the y-axis as the dependent variable.
Law of Supply
The law of supply states that the higher the price, the larger the quantity supplied, all other things constant. The law of supply is demonstrated by the upward slope of the supply curve.
the supply curve often is approximated as a straight line to simplify analysis. A straight-line supply function would have the following structure:
Quantity = a + (b) Price
Quantity Supplied is a function of price.
where a and b are constant for each supply curve.
A change in price results in a change in quantity supplied and represents movement along the supply curve.
Law of supply can be understood with the following schedule and Curve.
According to law of Supply , ” Quantity suppliesd increases with the increase in price”.






Comments are closed.