This section of the chapter will explain the constraints faced by society, using a model called the production possibilities frontier (PPF). There are more similarities than differences between individual choice and social choice. As you read this section, focus on the similarities. Because society has limited resources (e.g., labor, land, capital, raw materials) at any point in time, there is a limit to the quantities of goods and services it can produce. Suppose a society desires two products, healthcare and education.
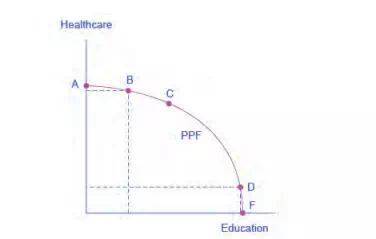
healthcare is shown on the vertical axis and education is shown on the horizontal axis. If the society were to allocate all of its resources to healthcare, it could produce at point A. But it would not have any resources to produce education. If it were to allocate all of its resources to education, it could produce at point F. Alternatively, the society could choose to produce any combination of healthcare and education shown on the production possibilities frontier. In effect, the production possibilities frontier plays the same role for society as the budget constraint plays for Alphonso.
Society can choose any combination of the two goods on or inside the PPF. But it does not have enough resources to produce outside the PPF. Most important, the production possibilities frontier clearly shows the tradeoff between healthcare and education. Suppose society has chosen to operate at point B, and it is considering producing more education. Because the PPF is downward sloping from left to right, the only way society can obtain more education is by giving up some healthcare. That is the tradeoff society faces. Suppose it considers moving from point B to point C. What would the opportunity cost be for the additional education? The opportunity cost would be the healthcare society has to give up. Just as with Alphonso’s budget constraint, the opportunity cost is shown by the slope of the production possibilities frontier. By now you might be saying, “Hey, this PPF is sounding like the budget constraint.” If so, read the following Clear It Up feature.
The Shape of the PPF and the Law of Diminishing Returns
The budget constraints presented earlier in this chapter, showing individual choices about what quantities of goods to consume, were all straight lines. The reason for these straight lines was that the slope of the budget constraint was determined by relative prices of the two goods in the consumption budget constraint. However, the production possibilities frontier for healthcare and education was drawn as a curved line. Why does the PPF have a different shape? To understand why the PPF is curved, start by considering point A at the top left-hand side of the PPF. At point A, all available resources are devoted to healthcare and none are left for education.
This situation would be extreme and even ridiculous. For example, children are seeing a doctor every day, whether they are sick or not, but not attending school. People are having cosmetic surgery on every part of their bodies, but no high school or college education exists. Now imagine that some of these resources are diverted from healthcare to education, so that the economy is at point B instead of point A. Diverting some resources away from A to B causes relatively little reduction in health because the last few marginal dollars going into healthcare services are not producing much additional gain in health. However, putting those marginal dollars into education, which is completely without resources at point A, can produce relatively large gains. For this reason, the shape of the PPF from A to B is relatively flat, representing a relatively small drop-off in health and a relatively large gain in education.






Comments are closed.