In companies, planning processes can result in increased output, higher precision, and faster turnaround for vital business tasks. A process is described as a set of steps that result in a specific outcome. It converts input into output. Process planning is also called manufacturing planning, material processing, process engineering, and machine routing. It is the act of preparing detailed work instructions to produce a part. It is a complete description of specific stages in the production process. Process planning determines how the product will be produced or service will be provided. Process planning converts design information into the process steps and instructions to powerfully and effectively manufacture products. As the design process is supported by many computer-aided tools, computer-aided process planning (CAPP) has evolved to make simpler and improve process planning and realize more effectual use of manufacturing resources.
Process Planning
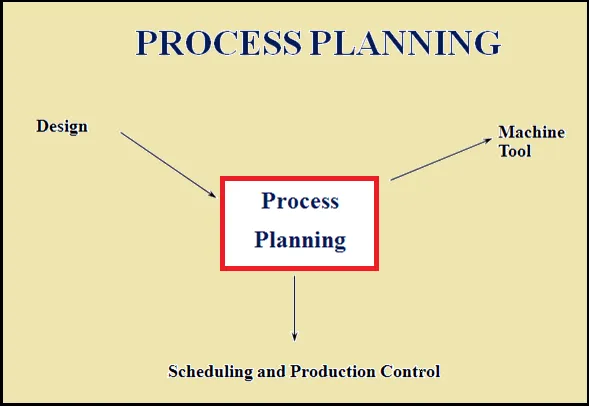
It has been documented that process planning is required for new product and services. It is the base for designing factory buildings, facility layout and selecting production equipment. It also affects the job design and quality control.
Objective of Process Planning: The chief of process planning is to augment and modernize the business methods of a company. Process planning is planned to renovate design specification into manufacturing instructions and to make products within the function and quality specification at the least possible costs. This will result in reduced costs, due to fewer staff required to complete the same process, higher competence, by eradicating process steps such as loops and bottlenecks, greater precision, by including checkpoints and success measures to make sure process steps are completed precisely, better understanding by all employees to fulfil their department objectives. Process planning deals with the selection of the processes and the determination of conditions of the processes. The particular operations and conditions have to be realised in order to change raw material into a specified shape. All the specifications and conditions of operations are included in the process plan. The process plan is a certificate such as engineering drawing. Both the engineering drawing and the process plan present the fundamental document for the manufacturing of products. Process planning influences time to market and productions cost. Consequently the planning activities have immense importance for competitive advantage.
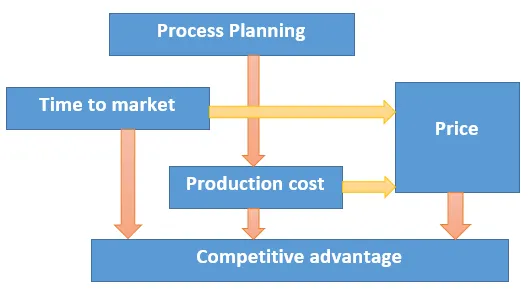
Effect of process planning on competitive advantage:
Principles of Process Planning
General principles for evaluating or enhancing processes are as follows:
v First define the outputs, and then look toward the inputs needed to achieve those outputs.
v Describe the goals of the process, and assess them frequently to make sure they are still appropriate. This would include specific measures like quality scores and turnaround times.
v When mapped, the process should appear as a logical flow, without loops back to earlier steps or departments.
v Any step executed needs to be included in the documentation. If not, it should be eliminated or documented, depending on whether or not it’s necessary to the process.
v People involved in the process should be consulted, as they often have the most current information.






Comments are closed.